Nuclear Power is basically an efficient way of producing heat by splitting apart uranium atoms. Every atom has bonds that hold its nucleus together; these bonds contain a lot of "stored" energy, so when nuclear fission occurs and breaks apart the atom, that energy is released as heat. This heat can be used to boil water into steam, and turn a turbine to produce electricity. |
 |
 |
Some pros of nuclear energy is the lack of greenhouse gas emissions and the efficiency of the plants. Greenhouse gases are becoming an increasing issue in modern day society due to concerns of global warming. Most of the energy that we as a society use is produced by coal or natural gases, which release excess amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Multiple new energy sources have attempted to find a solution to this increasingly more dangerous issue, such as wind power and solar power; however, these two examples are not very efficient and require other parameters, such as the right weather. Nuclear power fixes that; not only does nuclear fission not release harmful gases into the atmosphere, but it also can constantly make energy for years, all the time, without breaks. Also, wind turbines and solar panels take up loads of acres of land to produce a lot of electricity, whereas nuclear reactors don't need a lot of space to operate. |
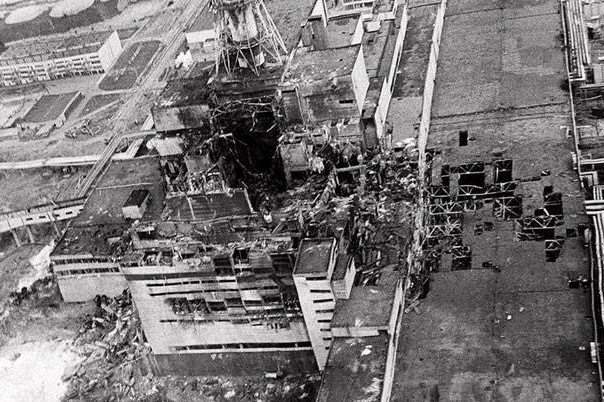
On the other hand, some cons of nuclear energy are the cost of creating reactors and the terrible reputation nuclear reactors have received in the past few decades. Let's discuss the cost: Today, if you wee to purchase a small nuclear reactor, you would have to fork over $750 million! Larger reactors obviously cost more, so needless to say, reactors are pretty dang expensive. Another factor in why nuclear power isn't currently powering everything we own is the public's opinion of nuclear reactors. There have been multiple nuclear power plant incidents over the years, most notably the Chernobyl incident and the Fukushima tsunami disaster. In Ukraine, 1986, one of the Chernobyl power plant's reactors exploded, sending radiation across the U.S.S.R. and essentially creating a zone in Ukraine that will remain unliveable for hundreds of years. Even though the incident was caused by a fault in the design that was soon fixed in every reactor since, the incident left a mark on how the world views nuclear power. On March 11, 2011, a tsunami struck the eastern Japanese coast, killing people and destroying loads of homes and infrastructure. The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant happened to be on the coast where the tsunami struck, and a day after the tsunami, the power plant exploded, sending radioactive materials across the Fukushima prefecture. To this day, work is still being done to decontaminate the surrounding areas and rebuild the cities and towns affected. These two events show the dangers of nuclear power, and while they are real dangers that should be taken into consideration, the risk has been minimized in the following years; however, due to the bad media coverage and poor reputation, the amount of nuclear power stations has decreased drastically over the past few years. |
 |
 |
Even though many countries are turning away from nuclear power due to the reasons listed above, some companies are attempting to make nuclear fission a more accessible and safe form of energy production. There are three major operations i found to be the most interesting: small modular reactors, advanced fission reactors, and fusion reactors. The first company is NuScale Power. NuScale's vision is set on making smaller, more affordable nuclear reactors. These reactors work similarly to traditional nuclear reactors, but produce a lot less energy due to the smaller size. Another advancement in nuclear technology is the work that the China National Nuclear Corp., TerraPower, and Terrestrial Energy are working on. These three companies' reactor designs use liquid sodium or molten salts as coolants inside the reactor instead of water for safety. Some even more advanced designs use gases such as helium for coolants; China has a helium-cooled reactor ready to be put on the grid this year! The final type of new nuclear reactors are the fusion reactors designed by the companies ITER, TAE Tech., General Fusion, and Commonwealth Fusion systems. These four companies are attempting to recreate conditions of the inside of the sun by creating and harnessing the energy of plasma. Magnets can potentially be used to confine the plasma into a densly packed area, however, progress is slow on these types of reactors due to the difficulties in achieving the temperature necessary to provide the energy. |
I'm very excited for the future of nuclear power, as it has a lot of benefits over other kinds of energy. While advancements may be slow due to a lack of public support, I think nuclear energy will greatly benefit the future of mankind. |